Spatio-Temporal Digital Signal Processing
for Focus Localization from array EEG
 Objective:
The detection of transient abnormalities in the EEG of epileptic patients, known as
"Interictal Epileptic Spikes", may be used to determine the location of
the "focus" or place of origin of the neurological malfunction.
Objective:
The detection of transient abnormalities in the EEG of epileptic patients, known as
"Interictal Epileptic Spikes", may be used to determine the location of
the "focus" or place of origin of the neurological malfunction.
Epileptic Focus localization is important in the planning and
performance of resective brain surgery for epilepsy.

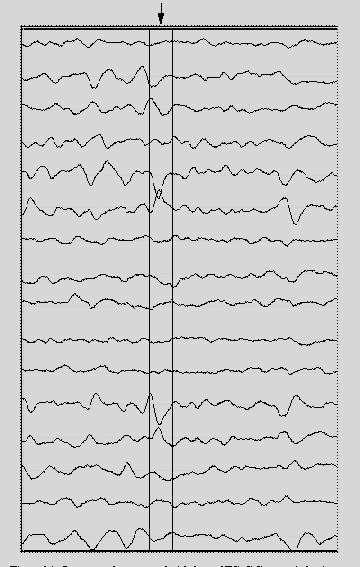
Hypothesis: Interictal Epileptic "spikes"
like the one indicated above in the EEG record really represent events in the time-varying
surface potential field. These field events are characterized by their spatial and
temporal sharpness.
A "Bubble Diagram" displays a spatio-temporal EEG sample
from a 3 x 4 electrode array as a circle of radius proportional to the
magnitude of the voltage. Shaded circles are negative voltages.

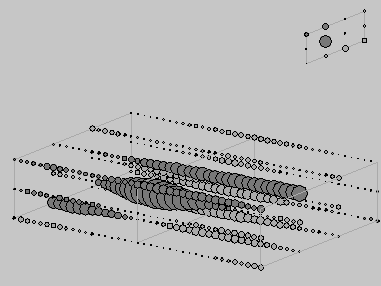
This Bubble Diagram of a focal interictal spike agrees with the hypothesis.

Method: Spatio-Temporal Laplacian
(STL) Transformation
Results
|